Data transmission refers to the transfer of data from one place to another. It requires a medium to transfer information.
The speed with which can be transmitted from one device to another is called data transmission speed or data transfer rate. Data rates are often measured in megabits or megabytes per second. These are usually abbreviated as Mbps and MBps, respectively. The medium on which the data is transmitted or the hardware and software required for the communication affects the speed of data transmission.
Transmission Media
Transmission media is the medium that carries the information from sender to receiver. Information is transmitted normally through electrical or electromagnetic signals.
What is the purpose of transmission media?
Transmission is a communication channel that carries the information from sender to the receiver.
It is broadly classified into two groups:
Guided / Wired Transmission Media
Unguided / Wireless Transmission Media
Guided / Wired Transmission Media
Guided media is a media that contain some conducting material or metal to carry data or signal. Many types of cables and wires fall under this category. For guide transmission media, the transmission capacity depends upon distance and whether the medium is a point to point or multipoint. The three guided transmissions commonly used for data transmission are:
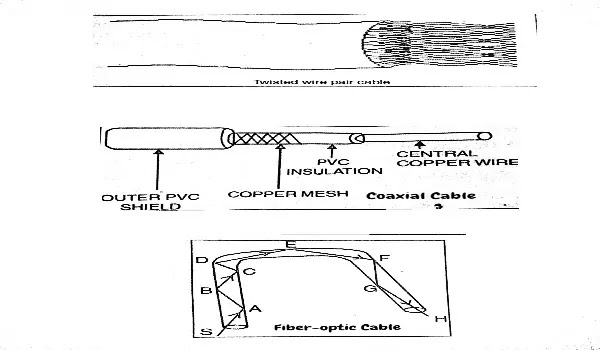
Twisted Wire Pair Cable
Coaxial Cable
Fiber Optic Cable
Twisted Wire Pair Cable
This is one of the most common transmission methods. These are used in local telephone communication and short-distance digital data transmission up to about 1km.
The data transmission speed of up to 9600 bits per second can be obtained for a distance of about 100 meters.
A twisted pair consists of two insulated copper wires arranged in a regular spiral pattern.
A wire pair acts as a single communication link.
Typically, a number of these pairs are bundled into a cable by wrapping them in a tough protection sheath.
For longer distances, local telephone lines are used but that reduces the transmission speed to about 1200 bits per second.
Insulated copper wires are twisted on each other to reduce interference by adjacent wires.
Out of all the communication channels for LAN, it is the easiest one to lay the network.
This cable suffers from noise and a low transmission rate.
The major disadvantages are the noise interface and a low transmission rate.
Characteristics of Twisted Wire Pair Cable
It may be used for transmitting either analog or digital signals.
Seed up to 9600 bits per second.
Up to 1000 devices can be accommodated.
Adequate for network span up to 1 km.
The repeater is required every 2 to 3 km.
The amplifier is required every 5 to 6 km.
The frequency range of 0 to 3.5 kHz.
The thickness of wires in a pair of from 0.12 to 0.9 mm.
Attenuation is Low.
Prone to interference and noise.
Inexpensive.
Easy to install.
Easy to tap.
For long-distance digital point to point signaling, data rates of up to a few Mbps are possible.
For every short distance, data rates of up to 100 Mbps are possible.
Applications of Twisted Wire Pair Cable
It is a commonly used medium in the telephone network.
It is the workhorse for communication within buildings.
Support voice traffic using analog signaling.
Support digital data traffic at modest data rates.
Support personal computers within the local area network.
Support digital signaling.
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable is the guided media used to carry signals of the higher frequency range as compared to twisted pairs.
They are groups of specially wrapped insulted wire lines.
A coaxial cable also uses two wires, but one is a tube woven from very fine strands of metal, the second one passes through the center along the length of the first.
It consists of a hollow outer cylindrical conductor that surrounds a single inner wire conductor.
The inner conductor is held in place by either regularly spaced insulting rings or solid dielectric material.
It is constructed to permit it to operate over a wide range of frequencies.
PVC insulation is used surrounding the central copper wire.
A thicker PVC material is used for shielding the metal sleeve.
The signal is transmitted by the inner copper wire.
Characteristics of Coaxial Cable
It is used to transmit is between 100 kHz to 500 MHz.
Offer much higher bandwidth.
Less prone to interference and crosstalk than twisted pair.
The repeater is required every 1 to 9 Km.
The amplifier is required every few Km.
Attenuation is high.
Capable of transmitting digital signals at very high rates of 10 megabits per second.
Extensively used over longer distances and support more stations on a shared line.
The well-packaged large cable can handle more than 16000 telephone lines simultaneously.
Less distortion or loss of signal.
More expensive than twisted-pair wiring.
More difficult to tap than twisted-pair wiring.
Applications of Coaxial Cable
Long-distance telephone transmission.
Distribution of television signals to individual Cable TV at homes.
Short-run computer system links.
Local Area Network.
Short-range connections between devices.
Using digital signaling, it provides high-speed input/output channels on a computer system.
It is used for long distances service by telephone companies and both baseband and broadband data transfer over a long distance and is immune to electrical noise.
Baseband Coaxial Cable transmits a signal at a time at a very high speed, while a broadband coaxial cable can transmit many simultaneous signals using different frequencies. A baseband cable transmits digital at a speed of about 2 million bits per second but must be amplified every 250 meters or so. It is mainly used for local area networks.
A broadband coaxial cable can transmit only analog signals, so it must be used in conjunction with a modem. It is not easy to use it in a network.
Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables are made of glass or transparent plastic. It has a cylindrical shape and consists of three concentric sections: the core, the cladding, and the jacket. The core is the inner section and consists of one or more very thin strands, or fibers made up of glass or plastic. Each core is surrounded by its cladding, made up of glass or plastic. The interface between the core and cladding acts as a reflector to confine light that would otherwise escape the core. The outermost layer suris rounded by a bundle of classed fiber called Jacket.
Fiber optic cables are as thick as human hair. The light enters at one end of the light pipe. After multiple reflections at various points inside the pipe, the light comes out without any significant loss of energy. On this cable, data is transmitted as pulses of light, which passes through the cables. These cables are secured and transmit large volumes of data over long distances.
Optical fibers carry a huge amount of data. Transmission is not distributed by electromagnetic interference and data are highly secure. Being optical in nature, fibers do not radiate electronic signals.
Semiconductor lasers transmit information in the form of light along optical fibers at the speed of light with no significant loss of intensity over light signals. At the outlet, the light signals are converted into light signals. At the outlet, the light signals after application are sent to the receiver.
Characteristics Of Optical Fiber
Transmission of the signal is at a very high-speed. Transmission speed is about 1Giga bits per second at a low error rate(1 in 109 bits).
A signal fiber in glass fiber cable has a thickness of about 2 microns. They occupy very little space in comparison to additional bulky copper wires.
The use of optical fibers is very cost-effective.
Optical fibers may be used to transmit either analog or digital signals. In analog signal transmission, the light intensity changes continuously whereas, in digital signal transmission, the light source is turned on and off.
Frequency ranges from 180 to 370THz.
Attenuation is low.
The repeater is required every 120Km.
Smaller Size and lighter weight.
Optical transmission is not affected by electromagnetic interference. Noise level is low and distortion is reduced to a very small amount.
Optical fibers are most useful for point to point one-way communication link. This is due to the reason that fiber optic cables cannot be tapped at various points.
Unauthorized tampering of information. Is very difficult. So they provide security against potential wire trappers.
Applications of Optical Fiber
Long distance telephone transmission.
Metropolitan trunks.
Subscribe loops.
Local Area Network.
What is the least expensive transmission media?
The most expensive and wildly used guided transmission media is twisted pair.

1 comments:
Click here for commentseasy to understand
Please do not entering spam link in the comment box ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon